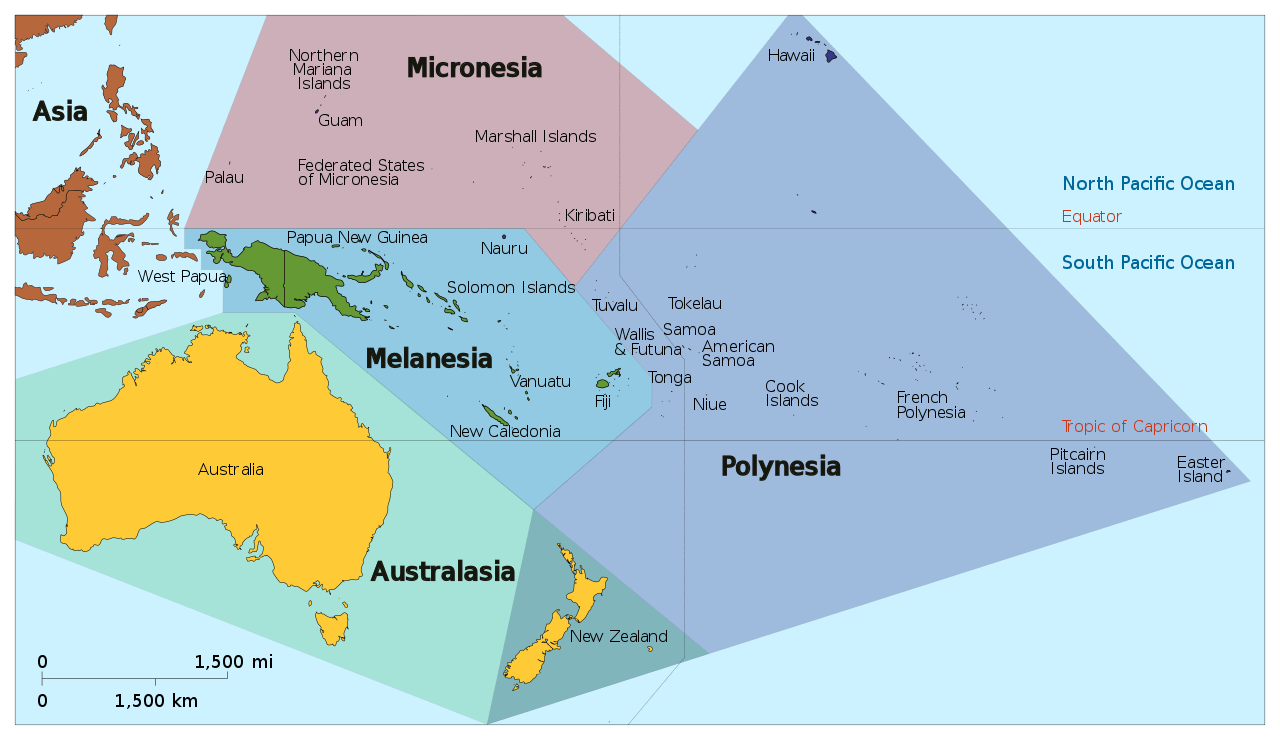
According to the United Nations, there are 14 different countries found within the region of Oceania in the Pacific Ocean. These countries are: Australia, Papua New Guinea, New Zealand, Fiji, the Solomon Islands, Micronesia, Vanuatu, Samoa, Kiribati, Tonga, the Marshall Islands, Palau, Tuvalu, and Nauru.
Oceania can be divided into four different subregions: Australia and New Zealand, Melanesia, Micronesia, and Polynesia. That’s a quick rundown of the countries within Oceania, but let’s take a more detailed look at these countries.
Australia
Photo: (https://pixabay.com/photos/australia-continent-aerial-view-62823/), WikiImages via Pixabay, Pixabay License (https://pixabay.com/service/license/)
Australia is the world’s sixth largest country in terms of landmass, with an area of around approximately 7,692,000 km² or 2,969,000 mi.² within its borders. Australia is the only country that is a continent by itself. Although Australia is the sixth largest country in terms of landmass, it is only the 51st largest country in terms of population, with approximately 25,379,000 people living there. Australia is rather sparsely populated, with the vast majority of its inhabitants living in coastal areas. It is thought that for almost 45,000 years, humans have lived on the Australian continent. A large desert area referred to as the outback covers the central portion of the continent, while coastal areas are often rain forests.
The Great Barrier Reef is located in Australia, which is home to some of the world’s most diverse aquatic life. The Australian continent is also home to many unique species of flora and fauna, many of which are marsupials. Marsupials are found almost exclusively in Australia and the surrounding areas, although some species of marsupials can be found other places in the world. Australia is home to over 750 different species of reptiles.
Papua New Guinea
After Australia, Papua New Guinea is the second most populous country in Oceania, with a population of around 8,586,000 people in 2019. Papua New Guinea shares the eastern half of the New Guinea island with Papua and West Papua. Papua New Guinea happens to be one of the most culturally diverse nations in the world, with its people speaking over 800 known languages. Papua New Guinea is the 54th largest country in the world in terms of land area, being approximately 462,800 km² in size. In terms of agricultural exports, the nation’s primary export is palm oil.
Papua New Guinea is home to many diverse species of animals in addition to diverse human populations. Several unique species of marsupials, including possums and kangaroos, are found only in Papua New Guinea.
New Zealand
New Zealand is the third largest country in terms of population in Oceania. The North Island and the South Island of New Zealand make up the majority of New Zealand’s land area, but approximately 600 smaller islands are also considered part of the country. New Zealand is home to approximately 4,968,000 people in 2019. Food products make up the majority of New Zealand’s exports. Around three-quarters of New Zealand residents are of European descent, with Maori, various Asian ethnicities, and Pacific peoples making up the remaining third of the population.
Because of New Zealand’s long period of geographic isolation, New Zealand has many unique and distinctive species of flora and fauna. Notable animals found in New Zealand include tuataras and skinks, as well as flightless birds like the Kiwi.
Fiji
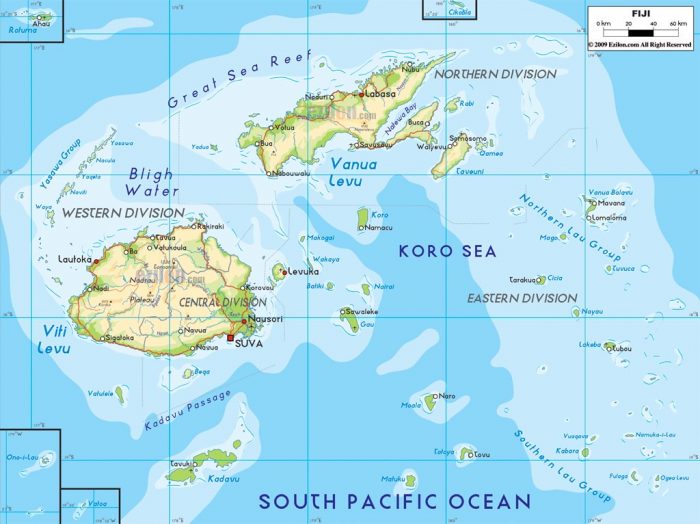
Photo: “Map of Fiji, Undated” by Nathan Hughes Hamilton (https://www.flickr.com/photos/nat507/12447704484), via Flickr, CC BY 2.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0/)
The islands of Fiji are found in Melanesia, approximately 2000 km northeast of New Zealand. Most of the islands that comprise Fiji were formed by volcanic activity around 150 million years ago. Fiji is home to around 912,000 people, according to the most recent census figures. In terms of land area, Fiji is the 151st largest country in the world with a total land area of 18,270 km² or 7050 mi.². The exporting of raw sugar, fish, and tourism account for much of Fiji’s economy. Most of Fiji’s population are native Fijians, from the Melanesian region, although some have Polynesian ancestry.
Solomon Islands
The Solomon Islands are found just to the east of Papua New Guinea, and they consist of six major islands combined with over 900 small islands. The Solomon Islands are considered part of Melanesia and they home to approximately 600,000 people. Important exports for the Solomon Islands are fish, palm oil, and copra. The vast majority of people in the Solomon Islands are of Melanesian descent, although some are Polynesian and/or Micronesian. Mammals are rare in the Soloman Islands, though reptiles and birds are quite abundant.
Micronesia
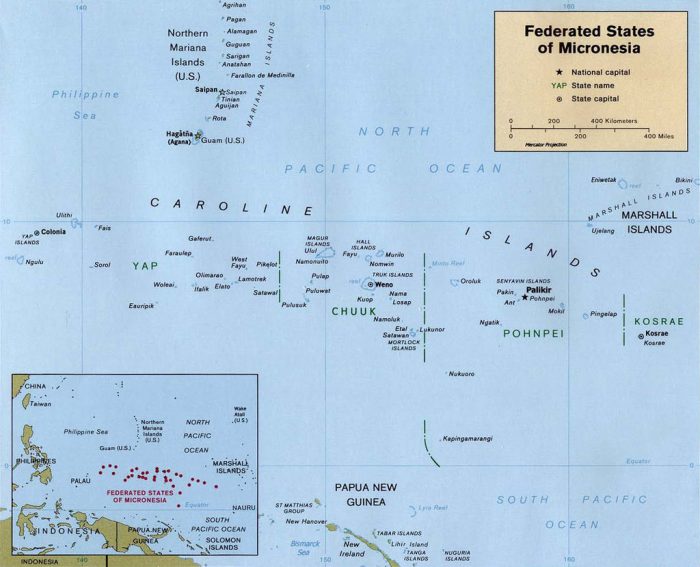
Photo: (https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=46492), By U.S. Central Intelligence Agency – Federated States of Micronesia (Political) 1999 from Perry-Castañeda Library Map Collection: Federated States of Micronesia Maps, via Wikimedia Commons Public Domain
The Federated States of Micronesia is a collection of four states: Chuuk, Pohnpei, Kosrae, and Yap. The nation of Micronesia should not be confused with the general geographical region, also referred to as Micronesia. Micronesia has a small population, only about 104,900 people live there. While the land area of Micronesia is quite small as well, 702 km2 (271 sq mi), its territory extends quite far, making it the 14th largest Exclusive Economic Zone in the world. Tuna fishing and tourism are the biggest drivers of the Micronesian economy.
Vanuatu
The Republic of Vanuatu is found east of New Guinea and west of Fiji. The nation is found in a volcanic archipelago, and about 273,000 people live in it. The total land area of Vanuatu is around 12,189 square kilometers or 4700 square miles. Vanuatu’s main exports include agricultural products like copra, kava, beef, and timber. Offshore financial services and tourism also account for much of the country’s income. Vanuatu’s national language is Bislama, though English and French are also widely spoken.
Samoa
The nation of Samoa is comprised of two main islands and four smaller islands. It is believed that the islands were settled by Lapita people around 3500 years ago, and in the intermittent time the people there developed their own cultural identity. Samoa is home to about 196,000 people. Native Samoans represent around 93% of the population, and Samoan and English are the official languages of the country. The services sector accounts for about 2/3rds of the country’s GDP.
Kiribati
Kiribati is found in Micronesia, and it is made out of 32 atolls and islands made out of reefs. The total population of Kiribati is around 110,000 people, and most of these people live on the atoll of Tarawa. It was in 1979 that the nation gained its independence from the United Kingdom.
Because Kiribati consists of many atolls stretching across thousands of kilometers, it is the only country in the world to be located within all four hemispheres. Currently, most of Kiribati’s exports are either fish or copra. Gilbertese is the official language of the country.
Tonga
Tonga is a nation found around 1800 kilometers from New Zealand, surrounded by Fiji and Samoa. Tonga was considered a British protected state until 1970, but the nation never surrendered sovereignty to any other nation. Tonga is home to around 100,650 people, as of a 2016 census. In terms of land area, Tonga is the world’s 175th largest country with a land area of around 748 square kilometers or 289 square miles. The vast majority of Tonga’s population lives on the main island of Tongatapu.
The Marshall Islands
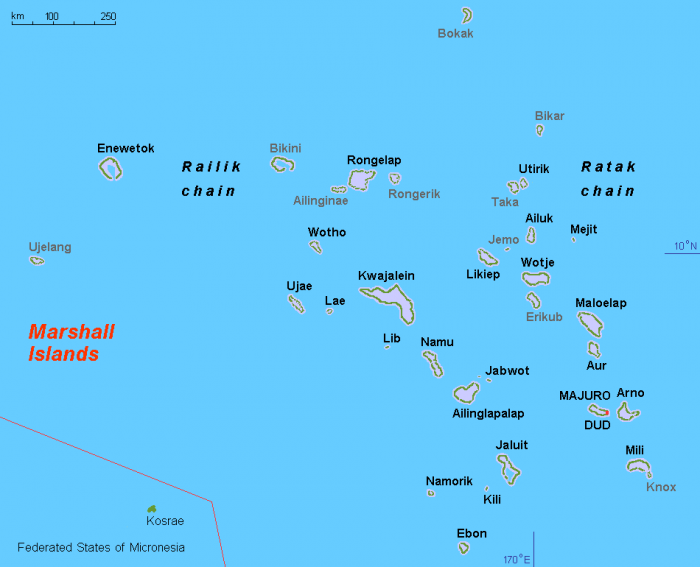
Photo: (https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=3721990) By Hobe / Holger Behr – Own work, via Wikimedia Commons, Public Domain
The Marshall Islands is found in Micronesia. The nation is comprised of 29 different coral atolls that are a conglomeration of over 1100 different islands. The population of Micronesia is around 53,100 people according to the last available census figures. The Marshall Islands was once a United States territory, gaining its self-governance from the US in 1979 and becoming a freely associated country in 1986. Agricultural products of the Marshall Islands include coconuts, tomatoes, taro, breadfruit, and melons. Tuna fishing is also a large part of the economy of the Marshall Islands. The Marshall Islands is home to over 300 species of fish, many of which are reef fish.
Palau
Palau is located in Micronesia, part of the Caroline Island chain. The nation shares some maritime boundaries with the Federated States of Micronesia, Indonesia, and the Philippines. The nation is currently freely associated with the United States. Around 21,500 people live in Palau. The main drivers of Palau’s economy are tourism, fishing, and subsistence agriculture. Palauan and English are the two languages of the country.
Tuvalu
Tuvalu is a country in Polynesia, located approximately halfway between Australia and Hawaii, northwest of the islands of Santa Cruz. According to the last available census figures, Tuvalu has a population of around 11,190 people. Three reef islands and six atolls make up the land area of Tuvalu. The citizens of Tuvalu live on 26 square kilometers or 10 square miles of land. In the late 19th century Great Britain declared the countries a British Protectorate, but in 1978 the nation gained its independence from the UK.
Nauru
Nauru is a nation in Micronesia, found to the northwest of Tuvalu and to the northeast of Papua New Guinea. The country is the third smallest country on Earth, just ahead of Vatican City and Monaco. It has only 21 square kilometers, or 8.1 square miles, of area within its borders. The nation is also the third smallest in terms of population, with only around 11,200 citizens. After World War 2, the country became part of a United Nations trusteeship, gaining its independence in 1968. Nauruan and English are the dominant languages of the country.









