Sophisticated Family Planning In Malaria Parasites
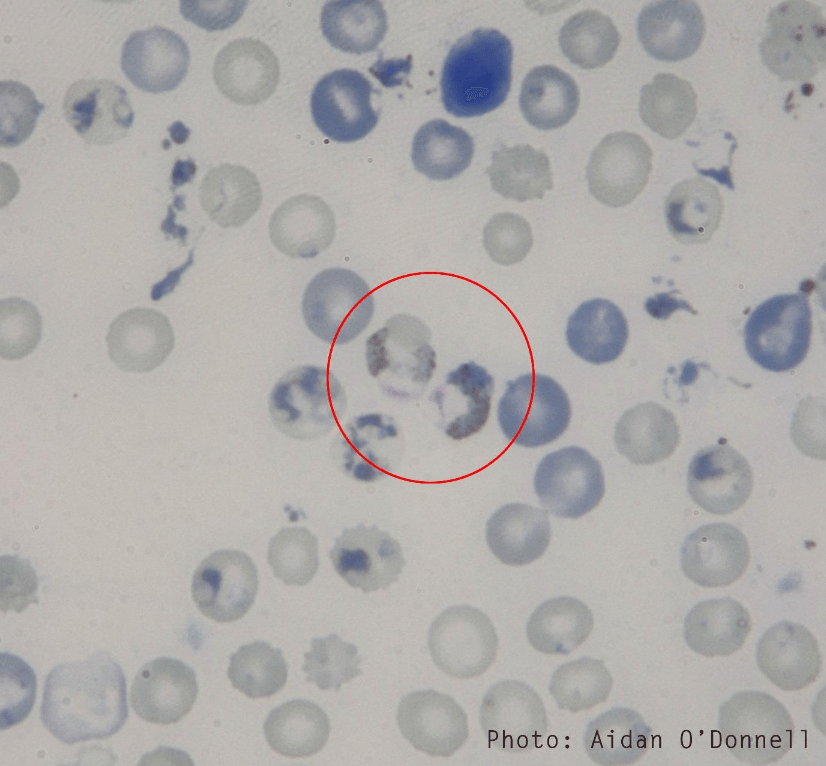
Malaria parasites can tell good times from bad times and plan their offspring accordingly. The reproductive strategy these disease-causing parasites use is more sophisticated than…
Read more