
The sugar found in RNA is ribose, whereas the sugar found in DNA is deoxyribose, both of which are 5-carbon sugars. Both types of sugars are important components of nucleotides. The sugars which can be found in nucleic acid are pentose sugars, part of what makes up DNA.
Deoxyribonucleic acid, or DNA, is often referred to as the building blocks for life. DNA carries the genetic instructions that allow all living organisms to function and reproduce. Yet DNA has a complementary molecule known as RNA. RNA and DNA work together in a complex relationship to produce a wide variety of life that we see in the world. DNA and RNA are similar in many aspects, but they also differ in key ways.
One of the primary differences between DNA and RNA is that RNA has a specific sugar that DNA does not. RNA has the sugar ribose in it. By contrast, DNA has the sugar deoxyribose. This is why RNA is called Ribonucleic Acid.
What sugar is found in RNA and DNA:
- Ribose (5-carbon sugar)
- Deoxyribose (5-carbon sugar)
What Is Ribose?
Ribose is referred to as a pentose monosaccharide, a simple sugar. It’s a carbohydrate, and it is composed of five carbon atoms. Unlike other monosaccharides, such as glucose, ribose isn’t oxidized when energy for cellular metabolism is required. Instead, ribose plays a critical role in the formation of molecules that transfer energy between parts of a cell. Ribose performs a variety of functions in addition to enabling the transference of energy. One of the ribose’s key functions is that it acts as the base for the genetic tool that makes proteins out of genes. It also serves as part of the backbone of chromosomes.
“The capacity to blunder slightly is the real marvel of DNA. Without this special attribute, we would still be anaerobic bacteria and there would be no music.” — Lewis Thomas
Ribose’s role in the transference of energy relates to something called the Krebs cycle, also referred to as the citric acid cycle. The Krebs cycle is a series of chemical reactions that derive energy out of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats. These chemical reactions are driven by different enzymes, and after the chemical reactions have taken place the energy that they generate is stored within the molecule dubbed NAD (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide).
The energized form of this molecule is referred to as NADH. Two ribose molecules are responsible for forming the structure of the NAD and NADH molecules. Without ribose, NADH would not be able to give its energy to the molecule known as ATP, adenosine triphosphate. ATP is the molecule that functions as the primary carrier of energy for cells, meaning that without ribose your cells would not be able to carry out all the functions that are required of them.
What is found in RNA but not DNA:
- Uracil, this is because RNA has cytosine and uracil as the pyrimidine bases. This is compared to DNA, which has cytosine and thymine as pyrimidine bases.
Ribose Makes Different Kinds of RNA
As mentioned before, ribose is a key component of ribonucleic acid. RNA is a critical part of the system that transforms DNA into proteins. While DNA is responsible for storing genetic information, it is RNA that codes for the synthesis of amino acids and carries information between ribosomes and DNA, allowing ribosomes to make proteins.
DNA is famous for its “double helix” structure, two intertwining strands with complementary bases. By contrast, RNA is a single-stranded molecule. There are other differences between DNA and RNA as well.
DNA is composed of a sugar-phosphate backbone and four bases: adenine, guanine, cytosine, and thymine. RNA is composed of a sugar-phosphate backbone and four bases as well, though one of them is different: adenine, guanine, cytosine, and uracil.
“DNA neither cares not knows. DNA just is. And we dance to its music.” — Richard Dawkins
RNA has uracil in it instead of thymine. When DNA bonds together, its bases always pair the same way. Adenine bonds with thymine, while guanine pairs with cytosine. Since RNA has uracil instead of thymine, uracil bonds with adenine in RNA.
RNA’s different structure means it can carry out tasks that DNA can’t. There are three primary types of RNA that are involved in the synthesis of proteins. These types of RNA are transfer RNA (tRNA), ribosomal RNA (rRNA), and messenger RNA (mRNA).
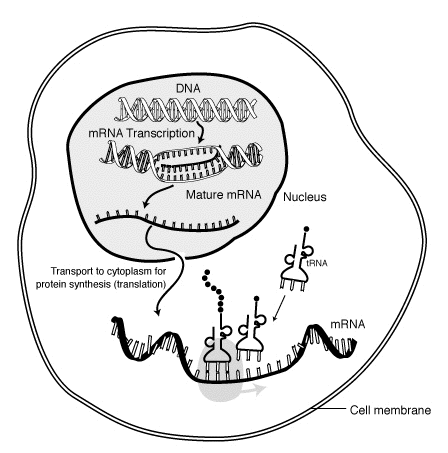
Ribose is found in mRNA, and mRNA plays an important role in protein synthesis for eukaryotic hours. Photo: Public domain
mRNA is responsible for carrying the genetic information between ribosomes and DNA. mRNA copies the genetic code from DNA and brings this information to the ribosomes, which are able to read the sequences of A, G, C and U. Thanks to this process the correct proteins will be synthesized by the ribosomes, and the mRNA will then typically break apart. mRNA is rather short-lived, as its only function is to ensure that the correct proteins are made when needed.
In contrast to mRNA, tRNA and rRNA are much more stable forms of RNA. Both eukaryotes and prokaryotes utilize tRNA and rRNA. These molecules are encoded into the DNA, and then they are synthesized into long molecules of RNA, which are cut up into smaller fragments. These small RNA fragments are important to the synthesis of proteins, even though they don’t carry instructions to the ribosomes.
rRNA is involved in the creation of ribosomes themselves, as it makes up approximately 60% of the mass of ribosomes. The rRNA provides a spot for the mRNA to anchor to, and it ensures the proper alignment of the mRNA, guided by the pairing of basis. It is also responsible for catalyzing the formation of peptide bonds between aligned amino acids during the process that synthesizes proteins.
tRNA is the third type of RNA, and it is also the smallest type. It is responsible for transporting the correct amino acids to the ribosome, carrying them to where the proteins are synthesized. The mRNA and the tRNA then pair their bases, which ensure that the correct amino acids are included in the synthesization of the polypeptide chain. It is extremely important for the correct amino acids to be parts of the synthesized proteins, as mutations in the rRNA or tRNA can cause problems for the entire cell.
“Genes are like the story, and DNA is the language that the story is written in.” — Sam Kean
It is speculated that RNA actually evolves before DNA. One of the reasons scientists believe this is the case is that RNA has a much simpler structure than DNA, and DNA is dependent upon RNA to function properly. This suggests that RNA was the genesis of the system of replication that cells depend on. Supporting this hypothesis is the fact that RNA is found in prokaryotic cells, which are generally believed to have evolved before eukaryotic cells. DNA likely evolved because it is superior in form to RNA. DNA’s double helix structure helps protect the genetic code from damage. It can quickly repair itself because if one strand is damaged, the other strand already has the blueprints to repair the structure.
While DNA might be a superior molecule for the purposes of storage, DNA could not function without RNA. RNA itself cannot function without the all-important ribose molecule, that allows it to maintain its structure.









