NO2 (Nitrogen Dioxide) Lewis Dot Structure
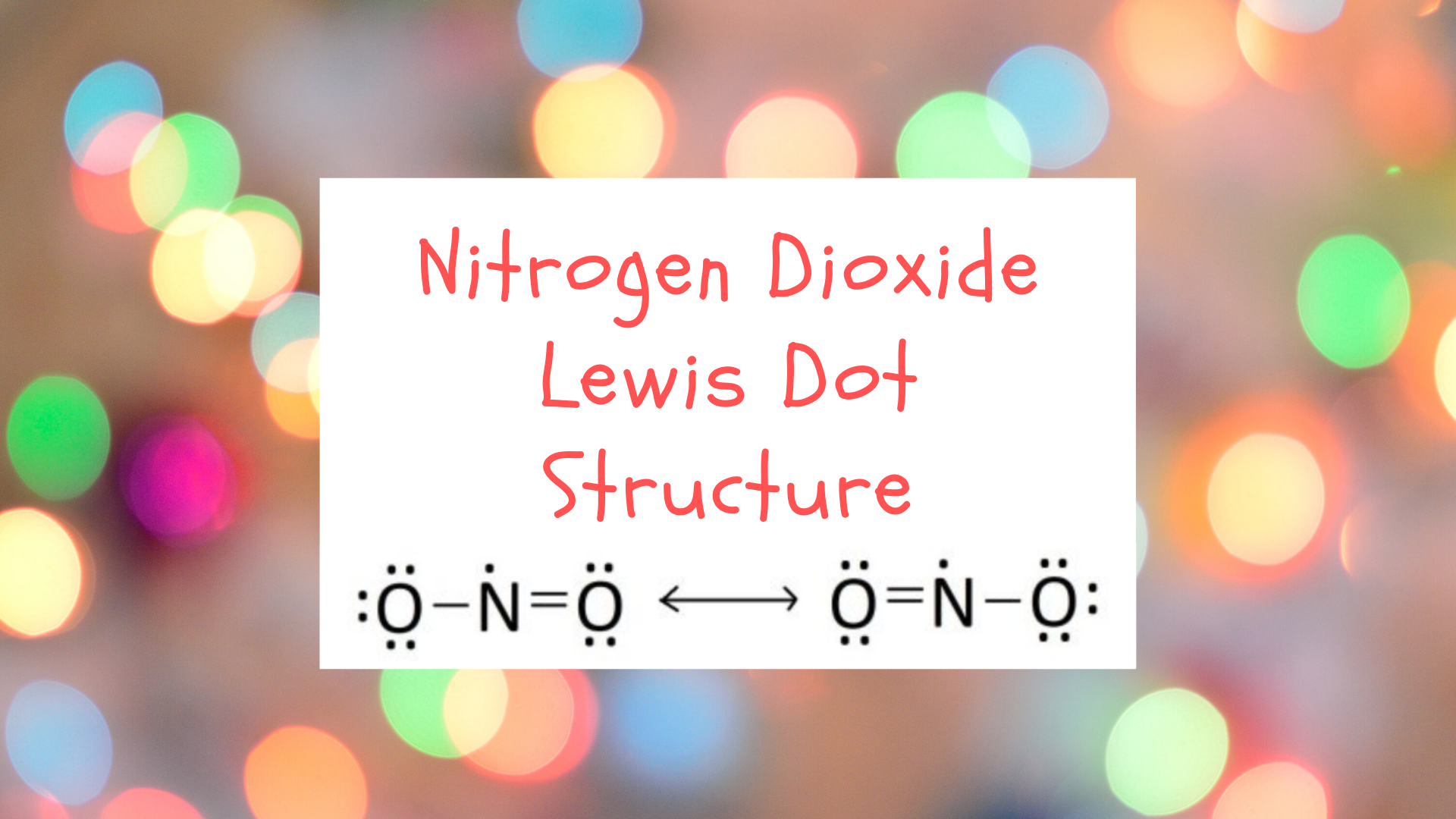
Nitrogen Dioxide (NO2) is a covalent compound that is composed of a central nitrogen atom single bonded to an oxygen atom and a double bond…
Read more

Nitrogen Dioxide (NO2) is a covalent compound that is composed of a central nitrogen atom single bonded to an oxygen atom and a double bond…
Read more

What causes lightning: When a positive and negative charge grows large enough in the sky you get lightning. This giant spark of electricity surges through…
Read more

The unity definition in art is the practice of combining parts of a painting to create a unified and compositionally complete piece of art. Unity…
Read more

Wind energy pros and cons can be separated into renewable, low operating costs, and energy independence for wind energy pros compared to intermittent energy, large…
Read more

NASA’s Juno spacecraft, that has been orbiting Jupiter since 2016, has sent us back some incredible information. The interior of Jupiter has been a mystery…
Read more

A CCL4 Lewis structure is a diagram that represents the electron configuration of covalently bonded compounds. Lewis structures are meant to provide a visualization of the atomic structure…
Read more

Photosynthesis produces both glucose (sugar) and oxygen as products in the chemical reaction. Plants use photosynthesis to take in sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide as…
Read more

The Roly-Poly bug is how the Armadillidium vulgare is commonly known. But this well-known bug also goes by different names, including potato bug, pill-bug, doodlebug,…
Read more

About a year ago there was some massive hype that giant pandas were taken off the endangered species list, but unfortunately, pandas are still very…
Read more

What are the factors of 36? If you remember any high school math then that question probably was not that hard (the answer is 1,…
Read more
Some examples of eubacteria include Streptococcus pneumoniae, the bacteria responsible for strep throat; Yersinia pestis, thought to be the cause of the black death; E. coli, found in the intestines…
Read more