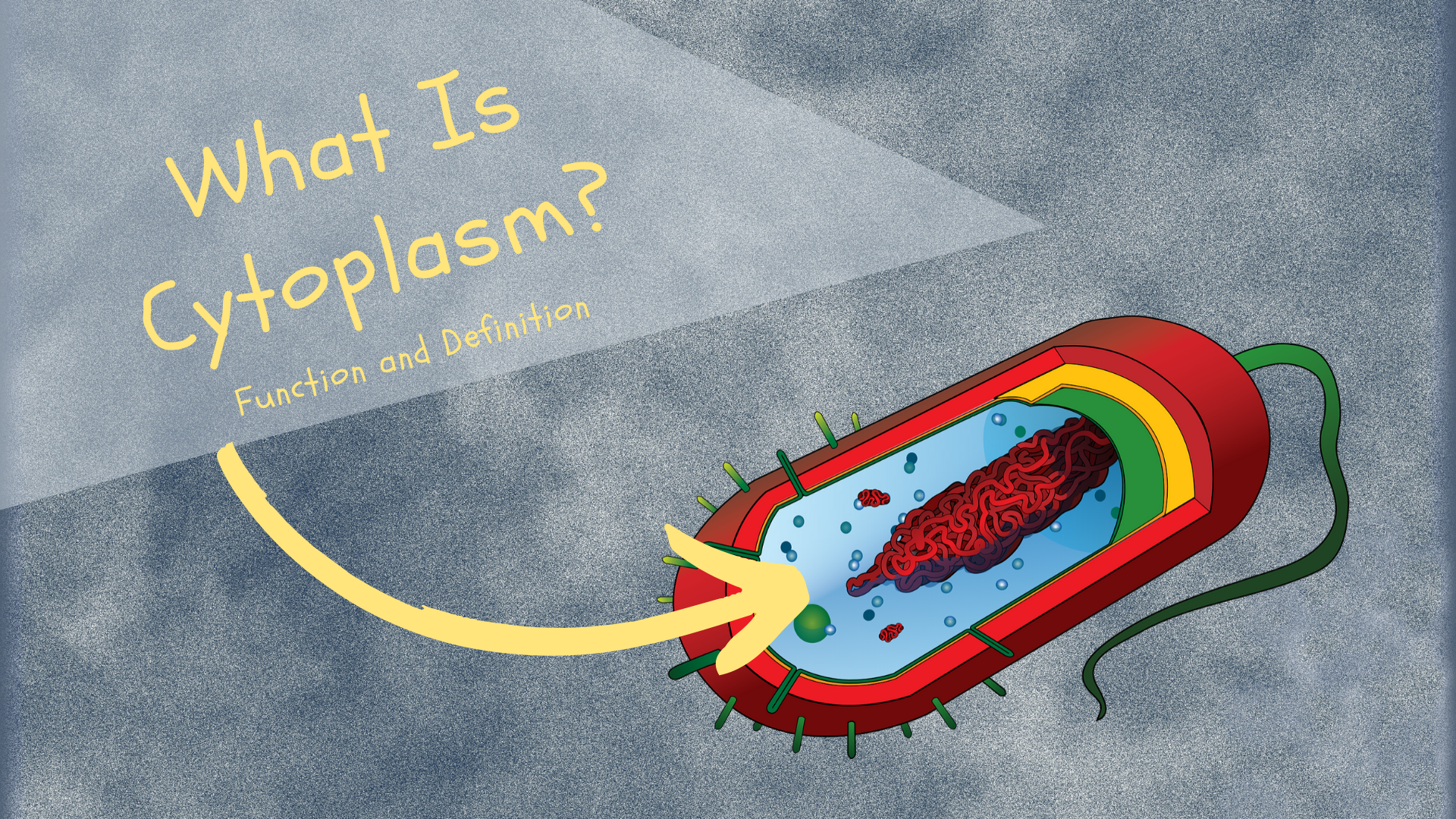
The function of cytoplasm is to act as the medium that fills your cells, it is a neutral jelly-like substance that acts to protect and house the cell parts within a cell. Cytoplasm is made up mostly of water and salt and is clear and colorless.
All cells are filled with a jelly-like substance known as cytoplasm. Usually, cytoplasm is colorless and see-through because it is composed of water at a level up to eighty percent. But what is its function?
“Our brains are wired to interpret shapes as faces and bodies. That’s why people see the Virgin Mary in the clouds or even in cheese sandwiches. It’s your cytoplasm, not some strange ectoplasm.” — Seth Shostak
Although cytoplasm is a thick and jelly-like substance, it becomes liquid if you stir it or shake it. The etymology of the word is “cyto” from the Greek words “kytos,” which means “a hollow, receptible, basket”; and “plasm,” which means “something molded or created.”
So, according to its etymology, cytoplasm is the substance that creates life. Its descriptive name is suitable because cytoplasm is the substance was all the organelles float and are then joined together thanks to a lipid membrane with two layers. This lipid membrane is both all in the cytoplasm and the organelles and the nucleus. Despite the cytoplasm’s gel-like appearance, this substance actually has a skeleton known, unsurprisingly, the cytoskeleton. Cells get their shape form the cytoskeleton.
But, what is cytoplasm made from other than water? Obviously, water wouldn´t be enough to sustain cytoplasm. While eighty percent of cytoplasm is effectively water, the rest of it is dissolved nutrients. Thanks to these dissolved nutrients cytoplasm are able to dissolve waste products.
What Is the Function of Cytoplasm?
Mainly, cytoplasm´s function is to support cellular molecules and cell organelles, which it also helps suspend.
But cytoplasm also has other key functions. These functions include the following cellular processes:
- Protein synthesis
- Glycolysis, which is the first stage of cellular respiration
- Mitosis
- Meiosis
Apart from these important cellular processes, cytoplasm also helps to move hormones and other materials around the cell. Cytoplasm also dissolves waste within the cell.
“The importance of the egg´s non-nuclear material – the cytoplasm – in early development is apparent in the consistent relation that is seen to exist between certain regions in the cytoplasm of a fertilized egg and certain kinds or directions of cell differentiation.” — John Gurdon
In order to understand how cytoplasm is able to carry out its many functions, we must examine how it is divided and what its components are.
How Is Cytoplasm Divided?
There are two main parts in the cytoplasm: the endoplasm and the ectoplasm.
The endoplasm is at the center of the cytoplasm and is where the organelles are suspended. The ectoplasm is the really jelly-like part of the cytoplasm that surrounds the endoplasm.
What Are the Components of Cytoplasm?
Not all cytoplasm cells have the same components.
The cytoplasm of prokaryotic cells has different components than that in eukaryotic cells.
Prokaryotic cells are the ones found in archaeans and bacteria. They are distinguished because they do not have a nucleus that is bound to a nucleus. The cytoplasm of prokaryotic cells is composed of everything that is inside the plasma membrane.
Eukaryotic cells are the ones found in animal and plant cells. The cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells have three components:
- Cytosol
- Organelles
- Cytoplasmic inclusions, which are different granules and particles
Let´s look at those three components are their functions in more detail:
- Cytosol: This component is either semi-fluid or fully liquid. It is located in the cell membrane but outside the nucleus
- Organelles: These components are small cellular structures each of which carries out a specific function. We will go into these functions later
- Cytoplasmic Inclusions: These components are temporarily suspended particles. They are made out of granules and macromolecules. Some of these inclusions are acids, enzymes, and protein; others are nutritive, such as lipids and glucose storage molecule or glycogen; and pigment granules, such as the melanin in skin cells
What Functions Are Carried Out by the Organelles?
Tiny organelles include the following:
- Mitochondria: these organelles both generate power and covert energy so that it can be used by the cell.
- Ribosomes: these organelles are made of proteins and RNA (Ribonucleic acid).
- Nucleus: this organelle is where all the cell´s hereditary information is stored. The nucleus is also responsible for controlling the growth and the reproduction of the nucleus.
- Lysosomes: these organelles are only found in animal cells; their function is to digest.
- Chloroplasts: these organelles are only found in eukaryotic cells; they are where photosynthesis takes place within these cells.
- Endoplasmic reticulum (ER): this organelle produces lipids and proteins and it helps to produce, process, and transport them.
- Golgi apparatus: this organelle is found in eukaryotic cells. Sometimes Golgi apparatus is referred to as the Golgi body or Golgi complex. Its main function is to manufacture some cellular products, but it also it warehouses them and ships them.
The organelles are supported by the cytoskeleton.
What Is Cytoplasmic Streaming?
Another important cellular process is cytoplasmic streaming, also known as cyclosis. This is the process whereby different substances circulate inside cells.
Cyclosis occurs in different types of cells, including the following:
- Plant cells
- Amoebae
- Protozoa
- Fungi
This streaming is influenced by different factors such as changes in temperature and light, or the presence of some hormones and chemicals.
“The nucleus has to take care of the inheritance of the heritable characters, while the surrounding cytoplasm is concerned with accommodation or adaptation to the environment.” — Ernst Haeckel
In the case of plant cells, cyclosis moves chloroplasts where they can be exposed to the largest amount of sunlight as possible. This is essential for photosynthesis. But in the case of other cell types, the cyclosis carries out a very different function. For example, in the case of amoebae and other protists, cytoplasmic streaming functions as a source of locomotion.
Cyclosis is also essential for the division of cells.
What Is a Cell Membrane?
The plasma membrane or cell membrane is what keeps the cytoplasm contained within a cell. It is thanks to this structure that cytoplasm does not spill out.
The lipid bilayer that makes out the cell membrane is formed by phospholipids. This layer keeps the cell isolated from all the fluid the surrounds it. However, the process known as endocytosis allows cytoplasm to add some of that external liquid and other molecules such as lipids, and proteins if necessary.