Examples Of Chemical Compounds In Science

A chemical compound is, for example, a chemical substance that is formed by the bonding of two or more different chemical elements. Every chemical compound has a…
Read more

A chemical compound is, for example, a chemical substance that is formed by the bonding of two or more different chemical elements. Every chemical compound has a…
Read more

Standard temperature and pressure (STP) refers to the internationally agreed-upon standard of measurement for experiments in chemistry. According to the International Union of Pure and…
Read more

The Lewis Dot Structure for O2 or dioxygen is as follows: O = O It’s a very simple structure, but how does one interpret this…
Read more

Carbon Tetrachloride can be expressed as CCl4, and it is made out of one carbon molecule and four chloride molecules. Carbon tetrachloride is nonpolar. Why…
Read more

Sound energy is the energy released by the vibration of objects, and measured in a unit called joules. Sound is a wave, and it has…
Read more

Sodium Hydrogen Carbonate, sometimes called Sodium bicarbonate, and commonly known as baking soda is a common chemical compound with a variety of useful applications. The…
Read more

Methane (CH4) is a non-polar hydrocarbon compound composed out of a single carbon atom and 4 hydrogen atoms. Methane is non-polar as the difference in electronegativities between carbon…
Read more
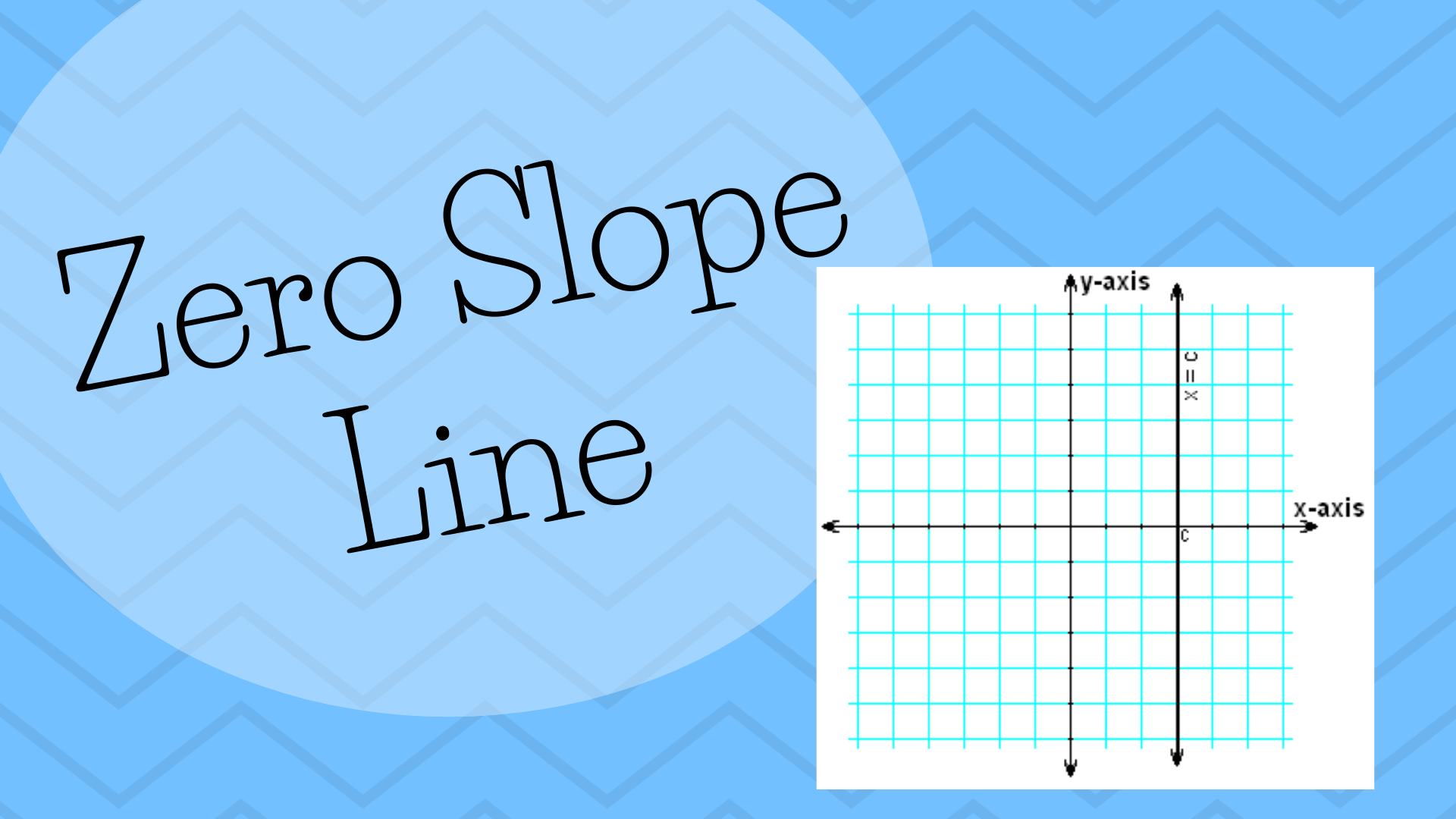
A zero slope line is a straight, perfectly flat line running along the horizontal axis of a Cartesian plane. The equation for a zero slope…
Read more

A plant cell diagram, like the one above, shows each part of the plant cell including the chloroplast, cell wall, plasma membrane, nucleus, mitochondria, ribosomes,…
Read more

In chemistry, the formula PV=nRT is the state equation for a hypothetical ideal gas. The ideal gas law describes the behavior of an ideal sample…
Read more
In chemistry, a physical change is a change to the form or structure of a chemical compound, but not to its chemical composition. An object…
Read more